In the first post of this blog series, I built an Azure OpenAI plugin for Genkit Go. This implementation relied on the new Azure OpenAI v1 API version. However, most Azure OpenAI users are likely using the previous API version 2024-10-21 because v1 is only two months old at the time of writing. In this blog post, I’ll show you how to adapt our Azure OpenAI plugin to support both v1 and 2024-10-21.
Dissecting Azure OpenAI 2024-10-21#
Let’s recall from the first blog post the key differences between OpenAI (including Azure OpenAI v1) and 2024-10-21:
When you access the model via the API, you need to refer to the deployment name rather than the underlying model name in API calls, which is one of the key differences between OpenAI and Azure OpenAI. OpenAI only requires the model name. Azure OpenAI always requires the deployment name, even when using the model parameter.
Our Azure OpenAI plugin already overrides the base URL with the correct Azure OpenAI endpoint URL and supports both Entra ID and API key authentication.
type AzureOpenAI struct {
*oai.OpenAI
APIKey string
TokenCredential azcore.TokenCredential
BaseURL string
}
func (a *AzureOpenAI) Init(ctx context.Context) []api.Action {
if a.APIKey == "" && a.TokenCredential == nil || a.APIKey != "" && a.TokenCredential != nil {
panic("Azure OpenAI plugin initialization failed: either APIKey or TokenCredential is required")
}
if a.BaseURL == "" {
panic("Azure OpenAI plugin initialization failed: Endpoint is required")
}
if a.OpenAI == nil {
// Overwrite base URL and provide API key
a.OpenAI = &oai.OpenAI{
APIKey: a.APIKey,
Opts: []option.RequestOption{
option.WithBaseURL(a.BaseURL),
},
}
// If no API key is provided, use TokenCredential (Entra) for authorization
if a.APIKey == "" {
// Satisfy the OpenAI plugin's requirement for a non-empty string
a.OpenAI.APIKey = "notused"
// Inject bearer token middleware
a.OpenAI.Opts = append(a.OpenAI.Opts, azure.WithTokenCredential(a.TokenCredential))
}
}
return a.OpenAI.Init(ctx)
}
Reviewing the REST API specs, we find the following discrepancies:
The request bodies for chat completion, embeddings, and other API endpoints in Azure OpenAI
2024-10-21do not include amodelfield like the OpenAI REST API does. As mentioned above,modelis replaced by the deployment name, which is specified in the URL path, not the request body.The API key is sent using the custom
api-keyheader, whereas OpenAI uses the standardAuthorizationheader.Azure OpenAI
2024-10-21requires the API version to be specified via theapi-versionquery string parameter.
All of these changes can be implemented by updating the RequestOption slice exposed by the embedded OpenAI plugin, as we’ve done previously when building our Azure OpenAI plugin.
Adding 2024-10-21 Support to Our Azure OpenAI Plugin#
First, we add a field to our plugin to store the deployment name.
type AzureOpenAI struct {
*oai.OpenAI
APIKey string
TokenCredential azcore.TokenCredential
BaseURL string
Deployment string
}
Next, we refactor the Init method to more easily distinguish between the initialization logic for v1 and 2024-10-21.
func (a *AzureOpenAI) Init(ctx context.Context) []api.Action {
if a.APIKey == "" && a.TokenCredential == nil || a.APIKey != "" && a.TokenCredential != nil {
panic("Azure OpenAI plugin initialization failed: either APIKey or TokenCredential is required")
}
if a.BaseURL == "" {
panic("Azure OpenAI plugin initialization failed: Endpoint is required")
}
if a.OpenAI == nil {
switch a.Deployment {
case "":
a.init()
default:
a.initWithDeployment()
}
}
return a.OpenAI.Init(ctx)
}
The logic to support both API versions in our plugin is straightforward: If the user creates the AzureOpenAI plugin without setting Deployment, the plugin uses the v1 API. If Deployment is set, the plugin uses the API version 2024-10-21.
Next, we add the initialization code for v1. It’s the same as before, just extracted into a separate method.
func (a *AzureOpenAI) init() {
// Overwrite base URL and provide API key
a.OpenAI = &oai.OpenAI{
APIKey: a.APIKey,
Opts: []option.RequestOption{
option.WithBaseURL(a.BaseURL),
},
}
// If no API key is provided, use TokenCredential (Entra) for authorization
if a.APIKey == "" {
// Satisfy the OpenAI plugin's requirement for a non-empty string
a.OpenAI.APIKey = "notused"
// Inject bearer token middleware
a.OpenAI.Opts = append(a.OpenAI.Opts, azure.WithTokenCredential(a.TokenCredential))
}
}
As mentioned above, the initialization logic for 2024-10-21 requires a few more changes to the RequestOption slice and must append the correct path with the deployment name to the base URL.
const apiVersion = "2024-10-21"
func (a *AzureOpenAI) initWithDeployment() {
// Build the effective base URL with deployment path
// Note: This should never fail unless BaseURL was a non-empty string that is not a valid URL
u, err := url.JoinPath(a.BaseURL, "openai", "deployments", a.Deployment)
if err != nil {
panic(fmt.Sprintf("unexpected error generating base URL: %v", err))
}
// Overwrite base URL, set "api-version" query parameter, and remove JSON attribute "model"
a.OpenAI = &oai.OpenAI{
APIKey: a.APIKey,
Opts: []option.RequestOption{
option.WithBaseURL(u),
option.WithQuery("api-version", apiVersion),
option.WithJSONDel("model"),
},
}
switch a.APIKey {
case "":
// Satisfy OpenAI's requirement for a non-empty string
a.OpenAI.APIKey = "notused"
// Inject bearer token middleware
a.OpenAI.Opts = append(a.OpenAI.Opts, azure.WithTokenCredential(a.TokenCredential))
default:
// Use the "api-key" header instead of "Authorization"
a.OpenAI.Opts = append(a.OpenAI.Opts,
option.WithHeader("api-key", a.APIKey),
option.WithHeaderDel("Authorization"))
}
}
We can update or add HTTP headers, change the base URL, and even remove headers or JSON body elements using option.WithHeaderDel or option.WithJSONDel. This allows us to remove the Authorization header and the model field from the request body.
model field isn’t strictly required—the field will be ignored by Azure OpenAI 2024-10-21. However, I prefer to remove it since this results in cleaner requests.With these changes, we’ve implemented all the necessary modifications to support Azure OpenAI 2024-10-21!
Enabling HTTP Debug Logs#
Before we update our sample application, I want to show you one more useful technique I use to analyze the HTTP traffic between my plugin and Azure OpenAI resources.
We add one more RequestOption:
func (a *AzureOpenAI) Init(ctx context.Context) []api.Action {
if a.APIKey == "" && a.TokenCredential == nil || a.APIKey != "" && a.TokenCredential != nil {
panic("Azure OpenAI plugin initialization failed: either APIKey or TokenCredential is required")
}
if a.BaseURL == "" {
panic("Azure OpenAI plugin initialization failed: Endpoint is required")
}
if a.OpenAI == nil {
switch a.Deployment {
case "":
a.init()
default:
a.initWithDeployment()
}
}
// Enable HTTP request/response logging if AZ_OPENAI_DEBUG_HTTP environment variable is set
debug := os.Getenv("AZ_OPENAI_DEBUG_HTTP")
if cmp.Or(debug == "1", strings.EqualFold(debug, "true")) {
a.OpenAI.Opts = append(a.OpenAI.Opts, option.WithDebugLog(log.Default()))
}
return a.OpenAI.Init(ctx)
}
The option.WithDebugLog() function allows us to specify a *log.Logger instance to which all HTTP requests and responses will be written. Using log.Default() writes these logs to stderr. Our code enables HTTP debug logging when the environment variable AZ_OPENAI_DEBUG_HTTP is set to true, TRUE, or 1.
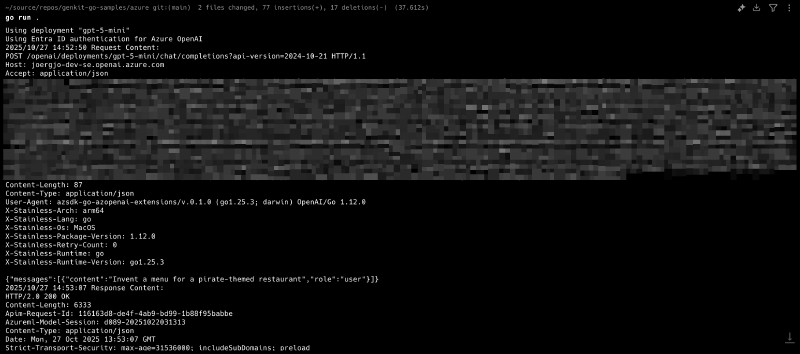
A Sample Application#
We can now extend our sample application to showcase the plugin for both API versions. We check for the presence of the environment variable AZ_OPENAI_DEPLOYMENT. If it is set, the application sets our plugin’s Deployment field accordingly and uses Azure OpenAI 2024-10-21. Otherwise, the sample uses v1 as before.
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"log"
"os"
"github.com/Azure/azure-sdk-for-go/sdk/azidentity"
"github.com/firebase/genkit/go/ai"
"github.com/firebase/genkit/go/genkit"
)
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
baseURL := os.Getenv("AZ_OPENAI_BASE_URL")
apiKey := os.Getenv("AZ_OPENAI_API_KEY")
if baseURL == "" || apiKey == "" {
log.Fatal("export AZ_OPENAI_BASE_URL and AZ_OPENAI_API_KEY to run this sample")
}
deployment := os.Getenv("AZ_OPENAI_DEPLOYMENT")
modelName := "gpt-5-mini"
switch deployment {
case "":
fmt.Println("AZ_OPENAI_DEPLOYMENT not set, using Azure OpenAI v1 API")
default:
modelName = deployment
fmt.Printf("Using deployment %q\n", deployment)
}
fmt.Println("Using Entra ID authentication for Azure OpenAI")
cred, err := azidentity.NewDefaultAzureCredential(nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("could not create credential: %v\n", err)
}
azOpenAI := &AzureOpenAI{
BaseURL: baseURL,
Deployment: deployment,
TokenCredential: cred,
}
g := genkit.Init(ctx, genkit.WithPlugins(azOpenAI))
model := azOpenAI.Model(g, modelName)
text, err := generate(ctx, g, model, "Invent a menu for a pirate-themed restaurant")
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("could not generate model response: %v\n", err)
}
fmt.Println(text)
fmt.Println("")
fmt.Println("---------------------------------------------------")
fmt.Println("")
fmt.Println("Using API key for Azure OpenAI")
// We already know that the API key is not empty.
azOpenAI = &AzureOpenAI{
BaseURL: baseURL,
Deployment: deployment,
APIKey: apiKey,
}
g = genkit.Init(ctx, genkit.WithPlugins(azOpenAI))
text, err = generate(ctx, g, model, "Invent a menu for a pirate-themed restaurant")
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("could not generate model response: %v\n", err)
}
log.Println(text)
}
func generate(ctx context.Context, g *genkit.Genkit, model ai.Model, prompt string) (string, error) {
// Simple chat completion
resp, err := genkit.Generate(ctx, g,
ai.WithPrompt(prompt),
ai.WithModel(model))
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
return resp.Text(), nil
}
v1 and using 2024-10-21 in the code. For v1, I have hardcoded the model as gpt-5-mini. Since a deployment in 2024-10-21 hides the actual model, you can use any model suitable for chat completion.Export the required environment variables and run the sample.
az login
export AZ_OPENAI_BASE_URL='https://<your-resource>.openai.azure.com/'
export AZ_OPENAI_API_KEY='<your-azure-openai-api-key>'
export AZ_OPENAI_DEPLOYMENT='<your-model-deployment>'
go run .
AZ_OPENAI_BASE_URL without any path. The correct path is added based on your deployment name at runtime!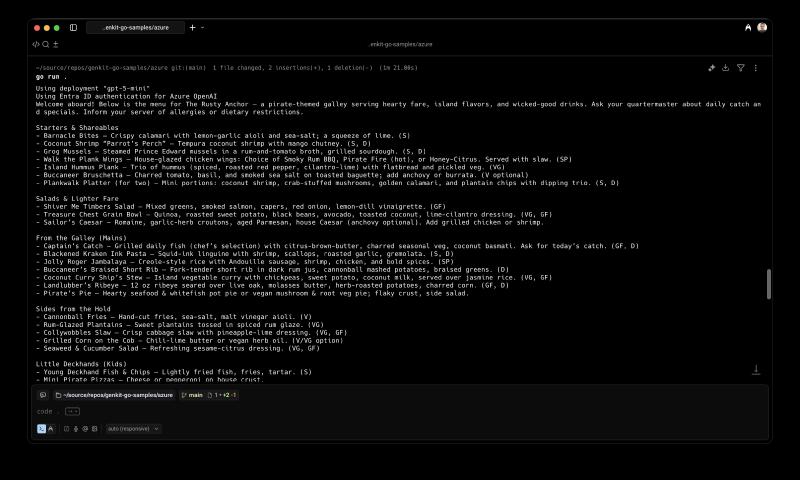
Summary#
This post explained how to extend our Azure OpenAI plugin for Genkit Go to support both the v1 and 2024-10-21 API versions. By leveraging the RequestOption slice from the OpenAI SDK, we can customize HTTP headers, query parameters, and request bodies to accommodate the differences between the two API versions. The plugin now detects which API version to use based on whether a deployment name is provided, making it flexible for users working with either version. I also demonstrated how to enable HTTP debug logging to help troubleshoot and analyze API interactions.